
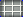
 Table of Data About Asteroids
Table of Data About Asteroids

for values specifications, see below
Data About Asteroids
| Name | Number | Diameter (km) | Semimajor axis (in AU) | Orbital period (in years) | Orbital eccentricity | Orbital inclination (in ° to the ecliptic) | Rotation period (in hr) | Mass 1015 kg | Spectral class |
|---|
| Ceres | 1 | 960x932 | 2.767 | 4.60 | 0.0789 | 10.58 | 9.075 | 870.000 | C |
|---|
| Pallas | 2 | 570x525x482 | 2.774 | 4.61 | 0.2299 | 34.84 | 7.811 | 318.000 | U |
|---|
| Juno | 3 | 240 | 2.669 | 4.36 | 0.2579 | 12.97 | 7.210 | 20.000 | S |
|---|
| Vesta | 4 | 530 | 2.362 | 3.63 | 0.0895 | 7.14 (Vesta further has a axis tilt of 27 degree) | 5.342 | 300.00 | U |
|---|
| Eugenia | 45 | 226 | 2.721 | 4.49 | 0.0831 | 6.61 | 5.699 | 6.100 | FC |
|---|
| Siwa | 140 | 103 | 2.734 | 4.51 | 0.2157 | 3.19 | 18.5 | 1.500 | C |
|---|
| Kleopatra | 216 | 217x94 | 2.793 | 4.67 | 0.2535 | 13.14 | 5.385 | | M |
|---|
| Ida | 243 | 58x23 | 2.861 | 4.84 | 0.0451 | 1.14 | 4.633 | 100 | S |
|---|
| Mathilde | 253 | 66x48x46 | 2.646 | 4.31 | 0.2660 | 6.71 | 417.7 | 103.3 | C |
|---|
| Eros | 433 | 33x13x13 | 1.458 | 1.76 | 0.2229 | 10.83 | 5.270 | 6.69 | S |
|---|
| Gaspra | 951 | 19x12x11 | 2.209 | 3.29 | 0.1738 | 4.10 | 7.042 | 10 | S |
|---|
| Icarus | 1566 | 1.4 | 1.078 | 1.12 | 0.8269 | 22.86 | 2.273 | 0.001 | U |
|---|
| Geographos | 1620 | 2 | 1.245 | 1.39 | 0.3356 | 13.34 | 5.222 | 0.004 | S |
|---|
| Apollo | 1862 | 1.6 | 1.471 | 1.81 | 0.5600 | 6.36 | 3.063 | 0.002 | S |
|---|
| Chiron | 2060 | 180 | 13.633 | 50.7 | 0.3801 | 6.94 | 5.9 | 4 | B |
|---|
| Shipka | 2530 | | 3.019 | 5.25 | 0.1237 | 10.10 | | | |
|---|
| Rodari | 2703 | | 2.194 | 3.25 | 0.0572 | 6.04 | | | |
|---|
| McAuliffe | 3352 | 2-5 | 1.879 | 2.57 | 0.3686 | 4.77 | | | |
|---|
| Mimistrobell | 3840 | | 2.249 | 3.38 | 0.0831 | 3.92 | | | |
|---|
| Toutatis | 4179 | 4.6x2.4x1.9 | 2.512 | 3.98 | 0.6339 | 0.47 | 130 | 0.05 | S |
|---|
| Castalia | 4769 | 1.8x0.8 | 1.063 | 1.10 | 0.4831 | 8.89 | | 0.0005 | |
|---|
| Otawara | 4979 | 5.5 | 2.168 | 3.19 | 0.1449 | 0.91 | | 0.2 | |
|---|
| AnneFrank | 5535 | 4 | 2.212 | 3.29 | 0.0643 | 4.25 | | | |
|---|
| Braille | 9969 | 2.2x1 | 2.341 | 3.58 | 0.4336 | 29.0 | | | |
|---|
| Itokawa | 25143 | about 1 | 1.324 | 1.52 | 0.2789 | 1.71 | | | |
|---|
data NASA's National Space Science Data Center (NSSDC)
(in alphabetical order)
- Diameter
- Asteroid diameter (in km). Many of the values are rough estimates only. When asteroid is spherical or roughly spherical, value is for the equator
- Mass
- Asteroid's mass (in kg15). All values are rough estimates only. Mass is not weight. Mass is the amount of matter in an object. Weight is mass on which gravity is acting. E.g. an object of similar mass (154 lb.) may have a weight of 154 lb. on Earth by on 26 lb only on Moon where gravity is 1/6th the one of Earth. Mass is used to characterize an object's inertia to acceleration, i.e. its resistance to be moved or have its direction changed
- Name
- Name of the asteroid (as defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU)). Usage now is to use both name and number of the asteroid (number first; 1 Vesta e.g.)
- Number
- Number of the asteroid (as defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU)). Usage now is to use both name and number of the asteroid (number first; 1 Vesta e.g.)
- Orbital eccentricity
- Measurement of the circularity of the orbit. Is computed by the formula: (aphelion - perihelion) / (2 x semimajor axis). A circular orbit would have a value 0
- Orbital inclination
- Angle between the asteroid orbit's plane and Earth's orbit's plane -which is the ecliptic (in ° compared to the ecliptic -which is 0)
- Orbital period
- Time for the asteroid to complete an orbit around the Sun between a vernal equinox and another one. Is the equivalent of the year for the Earth (in years)
- Rotation period
- Mean time the Sun takes to go from noon position to the next. Is the equivalent of the day for Earth (in hours)
- Semimajor axis
- Mean distance from Sun. Orbits of asteroids are not circles but ellipses; hence a point of the orbit is nearest to the Sun (perihelion) and one point is farthest of it (in AU (1 Astronomical Unit=92,960,116 miles -149,597,870 km)
- Spectral class
- Spectral class to which the asteroid belongs
Website Manager: G. Guichard, site 'Amateur Astronomy,' http://stars5.6te.net. Page Editor: G. Guichard. last edited: 12/28/2010. contact us at ggwebsites@outlook.com
![]() Table of Data About Asteroids
Table of Data About Asteroids![]()