
 Observation
Observation 
 Messier Objects Accessible To Binoculars and A 4.5" Newtonian Telescope
Messier Objects Accessible To Binoculars and A 4.5" Newtonian Telescope
Here are two lists of interest in relation with the Messier catalogue, that list of objects which was completed by the 18th century by French astronomer Charles Messier. Messier's catalogue officially was titled the 'Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters' as nebulae at the time represented any astronomical object that was not clearly localized and isolated. As he had been born by 1730 in Lorraine and his father a administrator in the Principalty of Salm-Salm in the Vosges mountain range, in eastern France, he witnessed the spectacular Comet Klinkenberg-Chéseaux by 1744 which had reached the -7th magnitude, which ignited his passion for astronomy. Hired as a draftsman for the French navy, he turned a skilled astronomical observer as he was eventually promoted to the chief astronomer of the Marine Observatory in Paris, where he pursued his interest in comets, discovering over a dozen of them, which earned him the nickname 'Comet Ferret' from King Louis XV. Charles Messier came to work with astronomer Joseph-Nicolas Delisle at the observatory of the Hotel de Cluny. He then turned into a prominent comet chaser. He studied 44, and discovered 20 of those between 1760 et 1801. Like a help for his searches -and also for his fellow comet chasers- he made a catalogue of the miscellaneous deep sky objects which could be confounded with a comet due to their diffuse aspect. The Crab Nebula was the first such object as it turned M1 thus. 110 objets thus are part of that famed 'Messier Catalogue.' Messier was honored by Napoleon I, in 1806, with the Légion d'Honneur and he died in Paris in 1817. The quality of the reflectors that the famed English astronomer William Herschel (1738-1822) was manufacturing for himself allowed him to resolve the 'nebulae' of Messier into stars. The Messier Catalogue, which was closed by 1966 only, nowadays turned a reference used by amateur astronomers worldwide. The 110 catalogued object are termed under the form Mxxx, M standing for Messier. The first of our following lists is the one of the Messier objects accessible through binoculars. The second one of the Messier objects accessible to, and resolved through a 4.5" reflector telescope, as data are also given about observation through a 60-mm refractor! Most other Messier objects are needing telescopes with a aperture superior to binoculars or a small telescope. A good, detailed list of the Messier objects has been put online by the French Société Astronomique de Bordeaux, as the text unluckily is in French only. A good source to get a picture for each Messier object before observation in the purpose of knowing what to look for like a general shape may be Wikipedia, at each Messier item. Abbreviations given for each object are the ones usually used by amateur astronomers in the Anglo-Saxon world. A guide to those abbreviations is given by the end of that tutorial. Of note that there is a window of about a week in mid-March where fashion recently developped the so-called 'Messier Marathon.' During the whole night, a observer is able to observe all the 110 Messier
objects. You will know too that the Hubble Space Telescope has not captured images of all 110 objects in the Messier catalog, but 93 of them only as of September 2017. A large part of our Messier objects are illustrated with a picture taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (coyright site 'Amateur Astronomy' based upon pictures NASA)
Of interest too in terms of deep sky objects accessibles to amateur astronomers, is the Caldwell catalogue dated 1995 (published by the Sky & Telescope magazine), a attempt of 109 deep sky objects by late Sir Patrick Alfred Caldwell-Moore, a prominent English amateur astronomer. That's a complement to the Messier with more bright, or southern hemisphere objects. Moore used Caldwell, its second surname like the catalog's name as the 'M' initial of Moore was no different to the one of Messier. localized Wikipedia pages, at 'Caldwell Catalogue' are of use and a good starting point like a search on a search engine also (while the Hubble Space Telescope has not taken images of every object in the Caldwell catalog, it had observed 95 of them as of late 2019; check with that NASA page: Explore - The Night Sky | Hubble’s Caldwell Catalog, which illustrates and document). At last, as far as the famed NGC catalogue is concerned, William Herschell systematically cataloged many of the objects he viewed in the night sky as his aunt Caroline discovered several comets and nebulas. John Herschell then took this aforementioned catalog of night-sky objects and reworked and expanded it into his General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars. This was the basis for the cataloging system still used today by astronomers, John Louis Emil Dreyer's 'New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars,' or the 'New General Catalogue' for short (which gives the NGC names of deep-sky objects). Since galaxies are extremely far away, astronomers rely on extremely bright objects, such as Type Ia supernovae and pulsating stars called Cepheids variables, as indicators of distance. To calculate how far away a distant galaxy is, scientists use known mathematical relationships between distance and other properties of objects, such as their total emitted energy. More objects useful for these calculations have emerged in recent years as there are now more than six dozen different indicators used to estimate distances. NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED), is a online repository containing information on over 100 million galaxies as the NED-D, a part of it, is dedicated to galaxies' distances

The following Messier objects are accessible to binoculars. Albeit faint and a unresolved, such objects are fine to search, and to observe! Objects which may already be resolved in binoculars are pointed to as such
- M2
- Aquarius, the Water Bearer
NGC 7089
Globular cluster, one of the richest and densest known; elliptical in shape.M2 is lying about 55,000 light-years away with a diameter of roughly 175 light-years, a population of 150,000 stars, and an age of 13 billion years. M2 is one of the largest clusters of its kind and one of the oldest associated with the Milky Way. It is bright enough that it can even be seen with the naked eye when observing conditions are extremely good
!!B vL;gpmbM;rrr;st eS;Lord Rosse-Dark area near core;* mags 13...
 | M2 |
- M3
- Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs
NGC 5272
Globular cluster, one of the most important in terms of the number of stars it contains. M3 is commonly acknowledged to be one of the most beautiful of all globular clusters. It contains as much a about 500,000 stars with a age 8 billion years! It also features a unusually large population of variable stars, and at least 170 of these are of the variety RR Lyrae, those standard candles. M3 also contains a relatively high number of so-called blue stragglers, those blue main sequence stars that appear to be young because they are bluer and more luminous. As all stars in globular clusters are believed to have formed together, only a difference in mass can give these stars their different color, that mass could ben stripped from a companion
!! eB;vL;vsmbM;st 11..;Lord Rosse-sev dark marks within 5' of center
 | M3 |
- M4
- Scorpius, the Scorpion
NGC 6121
Globular cluster, without a central concentration. It holds many white dwarfs
Cl 8 or 10 B* in line;rrr;Look for central bar structure
 | M4 |
- M5
- Serpens, the Serpent
NGC 5904
Globular cluster, one of the largest; M5 is 165 light-years in diameter as it lies some 25,000 light-years away
!! vB;L;eCM;eRi;st mags 11...;superb cluster
 | M5 |
- M6
- Scorpius, the Scorpion
NGC 6405
Butterfly cluster, a fine one; the brightest star at the 6.17th magnitude is orange as that cluster holds 2 variable stars. Already resolved with binoculars
Cl L;iR;lC;st7;10...;Butterfly cluster;51 members to 10.5 mag incl var* BM Sco
- M7
- Scorpius, the Scorpion
NGC 6475
open cluster discovered by Ptolemaeus, one of the closest to Earth; one begins to resolve it to binoculars
Cl vB;pRi;lC;*7...12;80 members to 10th mag;Fine naked eye cluster
- M8
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6523, Lagoon Nebula
Interstellar cloud which is lightened by a blue supergiant star; contains a fine open cluster, NGC 6530, which is made of young and very warm, forming stars of the type O and B
!!! vB;eL;eiF;w L Cl;Lagoon Nebula;Cl NGC 6530 invl;dark lane crosses neb
 | M8 |
- M9
- Serpens, the Serpent Holder
NGC 6333
Globular cluster, one of the closest to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy
B L;R;eCM;rrr;Dark neb B64 prominent to west
 | M9 |
- M10
- Serpens, the Serpent Holder
NGC 6254
Globular cluster, one of the closest to Earth
B vL;R;gvmBM;rrr;Lord Rosse reported dark lane in cluster
- M11
- Scutum, the Shield
NGC 6705, Wild Duck cluster
The richest open cluster, with 3,000 stars; very dense with a average distance between stars of 1 light-year only. M11 is one of the most star-rich and compact open cluster. The brightest M11 stars form a V shape that somewhat resembles a flock of ducks in flight; at its center lie many blue stars, the hottest and youngest of the cluster
!!Cl vB;L;iR;Ri;*9..;500 stars to 14th mag;Wild Duck cluster
 | M11 |
- M12
- Serpens, the Serpent Holder
NGC 6218
Globular cluster, one of the least dense in the Messier catalogue
vB vL;iR;gmbM;Somewhat loose structure
 | M12 |
- M13
- Hercules, the Heroe
NGC 6205, Hercules cluster
that is the famed Hercules cluster, one of the oldest Messier object, at 12 or 14 billion years. A message was sent to there to potential ETs from the Arecibo radiotelescope by 1974
!!eB vRi;vgeCM;*11...;Hercules cluster;Messier said round nebula contains no star
 | M13 |
- M15
- Pégasus, the Winged Horse
NGC 7078
Globular cluster, one the densest of our Milky Way Galaxy due to a gravitational collapse of its nucleus. One of the rare globulars to hold a planetary nebula, or Pease 1
! vB;vL;iR;vsmbM;rrr;st vS;Stars mags 13...
 | M15 |
- M16
- Serpens, the Serpent
NGC 6611, Star Queen or the Eagle Nebula
Open cluster and nebula; the place where the Hubble Space Telescope took its famed picture named 'The Pilars of Creation.' Young, blue O et B-type stars
L B;scattered Cl;neb invl;In Ser OB1;Star Queen or Eagle Nebula;stars mags 8...
 | M16 |
- M17
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6618, the Omega nebula, or the Swan Nebula
Cluster and very bright nebula due to young B-type stars with a HII region. M17 is located about 5500 light-years from Earth near the plane of the
Milky Way as it spans about 15 light-years
across. M17 also contains an open star cluster of 35 stars
!!! B;eL;eiF;2 hooked;Omega nebula;Swan Nebula;many F outer loops;use filter
 | M17 |
- M19
- Serpens, the Serpent Holder
NGC 6273
Oblate-shaped globular cluster, one of the closest to the Milky Way center
vB L;R;vCM;rrr;One of the most oblate globulars
- M21
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6531
Open cluster with a important central concentration (the distance between stars is of 1 light-year); resolved with binoculars- Cl pRi;lC;st9...12;In Sgr OB1;36 members to 12th mag
- M22
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6656
Globular cluster, one of the closest to the Earth; one of the rare globulars to harbour a planetary nebula and a zoo of objects like six planet-sized objects and two black holes. M22 was
discovered in 1665 by Abraham Ihle, or one of the first globulars ever to
be discovered. Fine aspect- vB vL;R;vRi;vmC;Stars mags 11...;one of finest globs
 | M22 |
- M23
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6494
Open cluster
Cl B;vL;pRi;lC;*10..;100 members to 13th mag
- M24
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6603, IC4715
Open cluster the border of which is very dense and relatively unascertained; a already remarkable sight in binoculars
eeL cloud of st and neb;Small Sagittarius Star Cloud; sev dark neb and NGC 6603 invl
- M25
- Sagittarius, the Archer
IC 4725
Open cluster; is already seeable in all its splendor (resolved?)
Cl pC;Contains U Sgr;Stars mags 6...10
- M27
- Vulpecula, the Little Fox
NGC 6853, the Dumbell Nebula
planetary nebula, the first one ever observed (in 1764); its name from its shape
!!vB vL;bi-N;iE;Dumbbell Neb;PK60-3.1;Lord Rosse drew 18* invl
- M28
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6626
Globular cluster, with 18 RR Lyrae-type variable stars; also, like M4, holds a millisecond pulsar; M 28 is located by 18,000 light-years away from Earth.
vB L;R;geCM;rrr;45' NW from Lambda Sgr;* mags 14...
 | M28 |
- M29
- Cygnus, the Swan
NGC 6913
Few dense open cluster, with 50 stars which are likely part of the Cygnus O-B Association
Cl P;lC;st L&S;About 20 stars mags 8...
- M30
- Capricornus, the Goat
NGC 7099
Dense globular cluster. Holds a dozen variable stars
! B;L;lE;gpmbM;st 12...16;Wm. Herschel saw very elliptical shape
 | M30 |
- M31
- Andromeda, Andromeda
NGC224, the Andromeda Galaxy (with M32, NGC1749 and M110, NGC205)
that is the famed Andromeda Galaxy with its two satellite galaxies. M31 is the sole galaxy seen naked eye from the northern hemisphere. It was observed since 905 A.D. by the Arab astronomer Abd-al-Rahman Al Sufi. Through Andromeda's Cepheids, Hubble was allowed to confirm the extra-galactic nature of what was then stiled 'nebulae.' Some advice that the best observation time for M31 is fall, which is explained by that the Andromeda Galaxy is reaching to the zenith. A 150mm telescope is needed to see the satellite galaxies M32 and M110 (M32 however is easily accessible to a 60-mm refractor; M110 is a dwarf elliptical galaxy)
M31 !!!eeB eL;vmE;Local Group;Andromeda Galaxy;nearest spiral. M32 vvB L;R;psmbMN;Companion to M31; Member of Local Group. M 110 vB vL;mE 165 degrees;vgvmbM;M31 Companion;UGC 426;H V 18; Member Local Group
 | M31 |
- M33
- Triangulum, the Triangle
NGC 598, the Pinwheel Galaxy
A spiral galaxy, one of the 3 large galaxies in the Local Group, with the Milky Way, and the Andromeda galaxies. M33 was the second galaxy identified like such by Hubble, in 1926. Need a 150mm telescope to be appreciated to its fair value
eB eL;R;vgbMN;Local Group;Pinwheel Galaxy;H V 17
- M34
- Perseus, Perseus
NGC 1039
Open cluster holding a hundred stars
Cl B;vL;lC;sC st9...;At least 80 true members;sev D* incl h1123 & O Struve 44
- M35
- Gemini, the Twins
NGC 2168
Open cluster holding several hundreds stars
Cl vL;eRi;pC;st9...16;Lord Rosse counted 300*;Orange * invl;NGC 2158 30' SW
- M36, M37, M38
- Auriga, the Charioteer
NGC1960 (with M37, NGC2099 and M38, NGC1912)
Three open clusters. Some sixty stars are lying in M36. M37 is very rich like a open star
M36 Cl B;vL;vRi;lC;*9..11;in Aur OB1;incl Struve 737 10.7''sep. M 37 !!Cl Ri;pCM;st L & S;Total population 500*;dark area near center. M 38 Cl B;vL;vRi;iF;st L & S;in Aur OB1;Burnham-shaped like Greek letter Pi
- M39
- Cygnus, the Swan
NGC 7092
Relatively loose open cluster which holds some thirty stars
Cl vL;P;vlC;*7...10;Large but loose cluster
- M41
- Canis Major, the Great Dog
NGC 2287
Open cluster which would have been known already since the time of Aristotle. It holds a hundred stars as it is located by some 4 degrees of Sirius
Cl vL;B;lC;st 8...;150 members to 13 mag;orange * near center
- M42
- Orion, the Hunter
NGC1976, the Hunter Nebula (with M43)
That Messier object is the famed Hunter Nebula as it located under Orion's Belt. M42 holds a very young open cluster with numerous stars in it. M43 is a diffuse nebula which is part of the Hunter Nebula
M 42!!! Theta Orion, the Hunteris and the great nebula M42;Trapezium* 6.7-7.7m;>50 var* invl;M 43 to NE. M 43 !vB;vL;R w tail;mbM*8;H III 1 ?;detached part of Orion, the Hunter Nebula
 | M42 |
- M44
- Cancer, the Crab
NGC 2632, Praesepe, or Beehive
A rich open cluster which is known since Antiquity. It was first resolved into stars by Galileo Galilei in 1610. Is said to contain more than 200 stars. Some tens of stars are resolved with binoculars. M44 appears like a rich field, of luminous stars as the field entirely settles into the field of view, with a small tendency to display a oblong form in one direction, which brings it there to overflow the field. One notes, among the set of stars of the cluster, one group of 3 and two groups of 2 which are neatly noticed
!!Praesepe, Beehive Cluster;200 memb to 14 mag
- M45
- Taurus, the Bull
NGC 1432/35, Mel 22, the Pleiades
A open cluster and nebula which is said to hold 500 stars as a dozen is visible naked eye. The 9 brighest have magnitudes between the 2.9th and the 5.5th. Asterope is a double star. The Pleiades are a fine cluster sight above Adelbaran
vvB vL;brilliant naked eye cluster;neb inv;Pleiades;nebys NGC 1432 and 1435 involved
 | M45 |
- M46, M47
- Puppis, the Ship's Stern
NGC2437 (with M47, NGC2422)
Two open clusters. At 1,600 light-years from Earth, M47 is a young -one of the least densely populated- open cluster contrasting blue and a few red giants in a region about 12 light-year across. First noticed about 1654 by Italian astronomer Giovanni Battista
Hodierna and later independently discovered by Charles Messier but with wrong coordinates as M47 was eventually re-discovered as NGC 2422 in 1934 and established the same in 1959 by
Canadian astronomer T. F. Morris. M47 by chance is seen close to M46, which lies at 5,500 light-years and contains a lot more stars at at least 500 stars present (it is fainter however due to its larger distance)
M46 ! Cl;vB;vRi;vL;PLNNB NGC 2438 on N edge;150 * 10-13 mag. M 47 Cl B;vL;pRi;st L & S;H VIII 38;Messier gave poor position;Struve 1121 & 1120 invl
- M50
- Monoceros, the Unicorn
NGC 2323
Open cluster with about 200 stars
Cl vL;Ri;pC;About 100 stars mags 9...14
- M52
- Cassiopeia, the Queen
NGC 7654
A open cluster the light of which is crossing acroos the interstellar medium which is very dense at that place in the Milky Way Galaxy
L Ri;mCM;*9..13;Messier saw neby there is none
- M53
- Coma Berenices, the Berenice's Hair
NGC 5024
Globular cluster, one of the farthest known, at 58,000 light-years; it holds 47 RR Lyrae-type variables
!B vC;iR;vvmbM;st 12...;1 deg NE of Alpha Comae Berenices
 | M53 |
- M54
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6715
Globular cluster which belongs to the Sagittarius Dwarf Galaxy, a satellite galaxy to our Milky Way Galaxy. M54 is extremely dense as it also holds 55 RR Lyrae-type variable stars
vB L;R;g;smbM;* mags 15...
- M55
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6809
Large globular cluster
pB L;R;vRi;vgbM;* mags 15...
 | M54 |
- M56
- Lyra, the Lyre
NGC 6779
Globular cluster
B L;iR;gvmCM;rrr;Stars 11...
 | M56 |
- M62
- Serpens, the Serpent Holder
NGC 6266
Very compact, elliptical globular cluster, and close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. That causes a slight shift of the cluster's nucleus relative to the halo
vB L;gmbM;rrr;Asymmetrical
 | M62 |
- M67
- Cancer, the Crab
NGC 2682
A open cluster, one of the oldest known, at 3.2 billion years. Open clusters generally tend to get dispersed earlier. Holds about 500 stars
! Cl vB;vL;eRi;lC;*10...15;500 memb to 16 mag;Mallas-dark spot near center
- M68
- Hydra, the Hydra
NGC 4590
Globular cluster. Holds some fifty variable stars, most of those of the RR Lyrae type, that type the most current among globular clusters
L eRi;vC;iR;rrr;st 13...;
 | M68 |
- M69, M70
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6637 (with M70, NGC 6681)
Globular cluster, it was first observed in the southern hemisphere. It features a relatively strong metallicity. M70 is lying relatively close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy as it is slightly deformed due to the gravitational forces. It holds a very dense nucleus as, like other globulars, it endured a gravitational collapse in the past. It is relatively hard to observe in the northern hemisphere
M 69 B L;R;rrr;*14..16;. M 70 B pL;R;gbM;Curved arc of stars to NE;* mags 14...
 | M69 |
 | M70 |
- M71
- Sagitta, the Arrow
NGC 6838
Globular cluster; it holds no variable, and none of the RR Lyrae type, which is rare in terms of a globular cluster
Cl vL;vRi;pmC;*11...16;Arrowhead shape; stars have few metals
 | M71 |
- M72
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC6981 (with M73, NGC6994)
Globular cluster, one of the farthest known, and located well beyond the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. It holds some 40 variable stars, most of those of the RR Lyrae type. M73 is a few dense open cluster. Relatively few visible
M 72 pB pL;R;gmCM;rrr;3 deg WSW of NGC 7009. M 73 Cl eP;vlC;No neb;4 or 5 10th mag stars; Messier saw neby but there is none; not a cluster
 | M72 |
- M75
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC6864
Globular cluster, one of the densest known, or of class I; it lies around 67,000 light-years away from Earth, having a luminosity allowing to easy photographs; discovered in 1780 by Pierre Méchain
B pL;R;vmbMBN;rr;* mags 17...
 | M75 |
- M78
- Orion, the Hunter
NGC2068
The brightest planetary nebula in the sky. It is located approximately 1600 light-years away and lying just to the upper left of the three stars that make up the Orion's Belt
B L;wisp;gmbN;3* inv;r;Comet shaped;2 10mag * invl; 53'' sep
- M79
- Lepus, the Hare
NGC1904
Globular cluster, one the rare located elsewhere than relatively close to the Milky Way's center. It is possible it belong indeed to the Great Dog Dwarf Galaxy, a satellite galaxy to our Galaxy. M79 is located 41,000 light-years from Earth as it contains about 150,000 stars packed into an area measuring only 118
light-years across. It was English astronomer William Herschel who resolved the stars in M79 4 years after its discovery
pL eRi;eC;rrr;Stars vF
 | M79 |
- M80
- Scorpius, the Scorpion
NGC6093
Very populated globular cluster, with several thousands of stars, and one of the densest. It looks like a comet
vB L;vmbM;rrr;st 14...;Extremely rich and compressed
 | M80 |
- M92
- Hercule
NGC6341
Globular cluster, one of the finest to observe. Very important central concentration du centre. One of the brightest globular clusters in the Milky Way, it is
visible to the naked eye under good observing conditions. It is very tightly
packed with stars, containing some 330,000 stars in total. M92 is also one of the oldest star clusters in our surrounding, with a age almost the one of the Universe
vB vL;eCM;st 12...;Lord Rosse saw spiral structure
 | M92 |
- M93
- Puppis, the Ship's Stern
NGC2447
Open cluster formed of 80 stars
Cl L;pRi;lC;st8...13;63 members to 13 mag;wedge shaped center
- M101
- Ursa Major, the Great Bear
NGC5457
A spiral galaxy which is seen right from above
pB vL;iR;g;vsmbM;BSN;P w NGC 5474;SN 1909;spir galax w one heavy arm;B knot E
 | M101 |
- M103
- Cassiopeia, the Queen
NGC581
Relatively few dense open cluster, and sparsed (with about 40 stars). A very bright double star is seen at the foreground as it is not part of the cluster
Cl pL;B;R;Ri;*10..11;in Cas OB8;incl Struve 131 6-9m 14''
- M107
- Serpens, the Serpent Holder
NGC6171
Globular cluster which holds about 25 variables. Stars within M 107 are not packed as tightly as in other clusters. Non-resolved?
L vRi;vmC;R;rrr;H VI 40
 | M107 |
The following Messier objects are accessible to a 4.5" refractor telescope as such a telescope allows to resolve the objects in stars. Data about observation through a 60-mm refractor are also given as and when available. It looks possible, generally, that a good such refractor give access to the whole of the list
- M3
- Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs
NGC 5272
Globular cluster, one of the most important in terms of the number of stars it contains. The nucleus is resolved to the cluster's borders. M3 is commonly acknowledged to be one of the most beautiful of all globular clusters. It contains as much a about 500,000 stars with a age 8 billion years! It also features a unusually large population of variable stars, and at least 170 of these are of the variety RR Lyrae, those standard candles. M3 also contains a relatively high number of so-called blue stragglers, those blue main sequence stars that appear to be young because they are bluer and more luminous. As all stars in globular clusters are believed to have formed together, only a difference in mass can give these stars their different color, that mass could ben stripped from a companion
!! eB;vL;vsmbM;st 11..;Lord Rosse-sev dark marks within 5' of center
 | M3 |
- M4
- Scorpius, the Scorpion
NGC 6121
Globular cluster, without a central concentration. It holds many white dwarfs
Cl 8 or 10 B* in line;rrr;Look for central bar structure
 | M4 |
- M6
- Scorpius, the Scorpion
NGC 6405
Butterfly cluster, a fine one; the brightest star at the 6.17th magnitude is orange as that cluster holds 2 variable stars
Cl L;iR;lC;st7;10...;Butterfly cluster;51 members to 10.5 mag incl var* BM Sco
- M7
- Scorpius, the Scorpion
NGC 6475
open cluster discovered by Ptolemaeus, one of the closest to Earth; one accedes to some thirty stars
Cl vB;pRi;lC;*7...12;80 members to 10th mag;Fine naked eye cluster
- M8
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6523, Lagoon Nebula
Interstellar cloud which is lightened by a blue supergiant star; contains a fine open cluster, NGC 6530, which is made of young and very warm, forming stars of the type O and B. A UHC filter is useful for such that type of nebula
!!! vB;eL;eiF;w L Cl;Lagoon Nebula;Cl NGC 6530 invl;dark lane crosses neb
 | M8 |
- M11
- Scutum, the Shield
NGC 6705, Wild Duck cluster
The richest open cluster, with 3,000 stars; very dense with a average distance between stars of 1 light-year only. The brightest M11 stars form a V shape that somewhat resembles a flock of ducks in flight; at its center lie many blue stars, the hottest and youngest of the cluster
!!Cl vB;L;iR;Ri;*9..;500 stars to 14th mag;Wild Duck cluster
 | M11 |
- M13
- Hercules, the Heroe
NGC 6205, Hercules cluster
that is the famed Hercules cluster, one of the oldest Messier object, at 12 or 14 billion years. A message was sent to there to potential ETs from the Arecibo radiotelescope by 1974
!!eB vRi;vgeCM;*11...;Hercules cluster;Messier said round nebula contains no star. With a 60-mm refractor, M13 is a fine, neat object which finely appears in sight surrounded with two stars. One perceives the cluster's granular aspect but it is not resolved. Density variations are seen on the cluster's perimeter
 | M13 |
- M17
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6618, the Omega nebula, or the Swan Nebula
Cluster and very bright nebula due to young B-type stars with a HII region. A UHC filter useful to accede to the color hues. M17 is located about 5500 light-years from Earth near the plane of the
Milky Way as it spans about 15 light-years
across. M17 also contains an open star cluster of 35 stars
!!! B;eL;eiF;2 hooked;Omega nebula;Swan Nebula;many F outer loops;use filter
 | M17 |
- M18
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6613
Open cluster with some twenty B3 stars; unresolved with a 4.5" Newtonian telescope. In Messier 18 the blue and white colours of the stellar population indicate that the cluster’s stars are very young, probably only around 30 million years old
Cl P;vlC;12 * mag 9-10; 1 deg S of M17 [1° au Sud de M17]
- M21
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6531
Open cluster with a important central concentration (the distance between stars is of 1 light-year)- Cl pRi;lC;st9...12;In Sgr OB1;36 members to 12th mag
- M22
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6656
Globular cluster, one of the closest to the Earth; one of the rare globulars to harbour a planetary nebula and a zoo of objects like six planet-sized objects and two black holes. M22 was
discovered in 1665 by Abraham Ihle, or one of the first globulars ever to
be discovered. Very fine in a 4.5" Newtonian telescope- vB vL;R;vRi;vmC;Stars mags 11...;one of finest globs
 | M22 |
- M24
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6603, IC4715
Open cluster the border of which is very dense and relatively unascertained
eeL cloud of st and neb;Small Sagittarius Star Cloud; sev dark neb and NGC 6603 invl
- M25
- Sagittarius, the Archer
IC 4725
Open cluster; is already seeable in all its splendor (resolved?)
Cl pC;Contains U Sgr;Stars mags 6...10
- M26
- Scutum, the Shield
NGC 6694
Open cluster; a area about void of any star, close to the core, is likely due to the presence of a opaque interstellar cloud
Cl cL;pRi;pC;st12..15;Finderscope will show why Messier included it;70 * to 14 m
- M29
- Cygnus, the Swan
NGC 6913
Few dense open cluster, with 50 stars which are likely part of the Cygnus O-B Association
Cl P;lC;st L&S;About 20 stars mags 8...
- M30
- Capricornus, the Goat
NGC 7099
Dense globular cluster. Holds a dozen variable stars
! B;L;lE;gpmbM;st 12...16;Wm. Herschel saw very elliptical shape
 | M30 |
- M31
- Andromeda, Andromeda
NGC224, the Andromeda Galaxy (with M32, NGC1749 and M110, NGC205)
that is the famed Andromeda Galaxy with its two satellite galaxies. M31 is the sole galaxy seen naked eye from the northern hemisphere. It was observed since 905 A.D. by the Arab astronomer Abd-al-Rahman Al Sufi. Through Andromeda's Cepheids, Hubble was allowed to confirm the extra-galactic nature of what was then stiled 'nebulae.' Some advice that the best observation time for M31 is fall, which is explained by that the Andromeda Galaxy is reaching to the zenith. A 150mm telescope is needed to see the satellite galaxies M32 and M110 (M32 however is easily accessible to a 60-mm refractor; M110 is a dwarf elliptical galaxy)
M31 !!!eeB eL;vmE;Local Group;Andromeda Galaxy;nearest spiral. M32 vvB L;R;psmbMN;Companion to M31; Member of Local Group. M 110 vB vL;mE 165 degrees;vgvmbM;M31 Companion;UGC 426;H V 18; Member Local Group
 | M31 |
- M33
- Triangulum, the Triangle
NGC 598, the Pinwheel Galaxy
A spiral galaxy, one of the 3 large galaxies in the Local Group, with the Milky Way, and the Andromeda galaxies. M33 was the second galaxy identified like such by Hubble, in 1926. Need a 150mm telescope to be appreciated to its fair value
eB eL;R;vgbMN;Local Group;Pinwheel Galaxy;H V 17
- M35
- Gemini, the Twins
NGC 2168
Open cluster holding several hundreds stars. A 4.5" telescope allows to NGC 2158, a neighbouring, denser open cluster
Cl vL;eRi;pC;st9...16;Lord Rosse counted 300*;Orange * invl;NGC 2158 30' SW
- M36, M37, M38
- Auriga, the CharioteerCocher
NGC1960 (with M37, NGC2099 and M38, NGC1912)
Three open clusters. Some sixty stars are lying in M36. M37 is very rich like a open star. Some stars seen with a 4.5" telescope
M36 Cl B;vL;vRi;lC;*9..11;in Aur OB1;incl Struve 737 10.7''sep. M 37 !!Cl Ri;pCM;st L & S;Total population 500*;dark area near center. M 38 Cl B;vL;vRi;iF;st L & S;in Aur OB1;Burnham-shaped like Greek letter Pi
- M39
- Cygnus, the Swan
NGC 7092
Relatively loose open cluster which holds some thirty stars
Cl vL;P;vlC;*7...10;Large but loose cluster
- M41
- Canis Major, the Great Dog
NGC 2287
Open cluster which would have been known already since the time of Aristotle. It holds a hundred stars as it is located by some 4 degrees of Sirius
Cl vL;B;lC;st 8...;150 members to 13 mag;orange * near center
- M42
- Orion, the Hunter
NGC1976, the Hunter Nebula (with M43)
That Messier object is the famed Hunter Nebula as it located under Orion's Belt. M42 holds a very young open cluster with numerous stars in it. M43 is a diffuse nebula which is part of the Hunter Nebula
M 42!!! Theta Orion, the Hunteris and the great nebula M42;Trapezium* 6.7-7.7m;>50 var* invl;M 43 to NE. M 43 !vB;vL;R w tail;mbM*8;H III 1 ?;detached part of Orion, the Hunter Nebula
 | M42 |
- M44
- Cancer, the Crab
NGC 2632, Praesepe, or Beehive
A rich open cluster which is known since Antiquity. It was first resolved into stars by Galileo Galilei in 1610. Is said to contain more than 200 stars. M44 appears like a rich field, of luminous stars as the field entirely settles into the field of view, with a small tendency to display a oblong form in one direction, which brings it there to overflow the field. One notes, among the set of stars of the cluster, one group of 3 and two groups of 2 which are neatly noticed
!!Praesepe, Beehive Cluster;200 memb to 14 mag
- M45
- Taurus, the Bull
NGC 1432/35, Mel 22, the Pleiades
A open cluster and nebula which is said to hold 500 stars as a dozen is visible naked eye. The 9 brighest have magnitudes between the 2.9th and the 5.5th. Asterope is a double star. The Pleiades are a fine cluster sight above Adelbaran
vvB vL;brilliant naked eye cluster;neb inv;Pleiades;nebys NGC 1432 and 1435 involved
 | M45 |
- M46, M47
- Puppis, the Ship's Stern
NGC2437 (with M47, NGC2422)
Two open clusters. At 1,600 light-years from Earth, M47 is a young -one of the least densely populated- open cluster contrasting blue and a few red giants in a region about 12 light-year across. First noticed about 1654 by Italian astronomer Giovanni Battista
Hodierna and later independently discovered by Charles Messier but with wrong coordinates as M47 was eventually re-discovered as NGC 2422 in 1934 and established the same in 1959 by
Canadian astronomer T. F. Morris. M47 by chance is seen close to M46, which lies at 5,500 light-years and contains a lot more stars at at least 500 stars present (it is fainter however due to its larger distance)
M46 ! Cl;vB;vRi;vL;PLNNB NGC 2438 on N edge;150 * 10-13 mag. M 47 Cl B;vL;pRi;st L & S;H VIII 38;Messier gave poor position;Struve 1121 & 1120 invl
- M48
- Hydrus, the Water Serpent
NGC 2548
Open cluster; ill-positioned by Messier, it was found back by 1959 only. Is low above the horizon
Cl vL;pRi;pmC;* 9..13;Messier wrong position by 4 deg in dec;50* 9-13mag;H VI 22
- M49
- Virgo, the Virgin
NGC 4472
A elliptical galaxy, one of the brightest in the Virgo Cluster (unresolved). Filled with an incredible 200 billion stars, at a distance of 56 million light-years and measuring 157,000 light-years across; it was the first member of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies to be discovered, and it is more luminous than any other galaxy at its distance or nearer. M49 is very yellow, which indicates that the stars within it are mostly older and redder than the Sun, and it is also rich of 6,000 globular star clusters
vB L;R;mbM;r;NGC 4467 @ 4.2';NGC 4470 @ 10.5';NGC 4465 @ 5.8'
 | M49 |
- M50
- Monoceros, the Unicorn
NGC 2323
Open cluster with about 200 stars
Cl vL;Ri;pC;About 100 stars mags 9...14
- M51
- Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs
NGC 5194, The Whirlpool Galaxy
face on galaxy with a interacting companion satellite galaxy. Unresolved with a 4.5" telescope
!!! Great spiral nebula;Whirlpool Gal;interacting pair;classic spiral
- M53
- Coma Berenices, the Berenice's Hair
NGC 5024
Globular cluster, one of the farthest known, at 58,000 light-years; it holds 47 RR Lyrae-type variables. Numerous stars resolved
!B vC;iR;vvmbM;st 12...;1 deg NE of Alpha Comae Berenices
 | M53 |
- M57
- Lyra, the Lyre
NGC 6720, the Ring Nebula
fine planetary nebula, which displays a ring made of ionized oxygen and nitrogen, and hydrogen. The central white dwarf is not accessible at the 15,8th magnitude
Ring neb B;pL;cE;Ring Nebula;central* var 14 to 16 mag;PK63+13.1. Starting at b Lyr, the field of M57 is easily enough found with a 60-mm refractor as the Ring Nebula is 'targeted' somehow by 3 stars at path's end. The nebula is seen like a blurred, grey object which finally is bright enough as the observer is inclined to believe he is seeing the nebula's ring, which is not necessarily true. M57 is at the 9.4th magnitude only
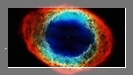 | M57 |
- M62
- Serpens, the Serpent Holder
NGC 6266
Very compact, elliptical globular cluster, and close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. That causes a slight shift of the cluster's nucleus relative to the halo. Numerous stars resolved
vB L;gmbM;rrr;Asymmetrical
 | M62 |
- M67
- Cancer, the Crab
NGC 2682
A open cluster, one of the oldest known, at 3.2 billion years. Open clusters generally tend to get dispersed earlier. Holds about 500 stars. Some stars resolved
! Cl vB;vL;eRi;lC;*10...15;500 memb to 16 mag;Mallas-dark spot near center
- M69, M70
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC 6637 (with M70, NGC 6681)
Globular cluster, it was first observed in the southern hemisphere. It features a relatively strong metallicity. M70 is lying relatively close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy as it is slightly deformed due to the gravitational forces. It holds a very dense nucleus as, like other globulars, it endured a gravitational collapse in the past. It is relatively hard to observe in the northern hemisphere
M 69 B L;R;rrr;*14..16;. M 70 B pL;R;gbM;Curved arc of stars to NE;* mags 14...
 | M69 |
- M71
- Sagitta, the Arrow
NGC 6838
Globular cluster; it holds no variable, and none of the RR Lyrae type, which is rare in terms of a globular cluster
Cl vL;vRi;pmC;*11...16;Arrowhead shape; stars have few metals
 | M71 |
- M75
- Sagittarius, the Archer
NGC6864
Globular cluster, one of the densest known. Belongs to class I; numerous stars resolved; it lies around 67,000 light-years away from Earth, having a luminosity allowing to easy photographs; discovered in 1780 by Pierre Méchain. Numerous stars resolved
B pL;R;vmbMBN;rr;* mags 17...
 | M75 |
- M78
- Orion, the Hunter
NGC2068
The brightest planetary nebula in the sky. The nebulosity is visible. M78 is located approximately 1600 light-years away and lying just to the upper left of the three stars that make up the Orion's Belt
B L;wisp;gmbN;3* inv;r;Comet shaped;2 10mag * invl; 53'' sep
- M79
- Lepus, the Hare
NGC1904
Globular cluster, one the rare located elsewhere than relatively close to the Milky Way's center. It is possible it belong indeed to the Great Dog Dwarf Galaxy, a satellite galaxy to our Galaxy. NGC 1904. M79 is located 41,000 light-years from Earth as it contains about 150,000 stars packed into an area measuring only 118
light-years across. It was English astronomer William Herschel who resolved the stars in M79 4 years after its discovery
pL eRi;eC;rrr;Stars vF
 | M79 |
- M80
- Scorpius, the Scorpion
NGC6093
Very populated globular cluster, with several thousands of stars, and one of the densest. It looks like a comet
vB L;vmbM;rrr;st 14...;Extremely rich and compressed
 | M80 |
- M83
- Hydra, the Hydra
NGC5236
A spiral galaxy with red regions (stellar formation HIII regions) and blue ones (with recently formed stars). Difficult to observe from the northern hemisphere. Unresolved?
vB vL;E55;esBMN;spir;Fast SupNova producer-4 in 50 yrs
 | M83 |
- M103
- Cassiopeia, the Queen
NGC581
Relatively few dense open cluster, and sparsed (with about 40 stars). A very bright double star is seen at the foreground as it is not part of the cluster
Cl pL;B;R;Ri;*10..11;in Cas OB8;incl Struve 131 6-9m 14''
ab about
alm almost
am among
annul annular or ring nebula
att attached
b brighter
bet between
biN binuclear
bn brightest to n side
bs brightest to s side
bp brightest to p side
bf brightest to f side
B bright
c considerably
chev chevelure
co coarse, coarsely
com cometic (cometary form
comp companion
conn connected
cont in contact
C compressed
Cl cluster
d diameter
def defined
dif diffused
diffic difficult
dist distance, or distant
D double
e extremely, excessively
ee most extremely
er easily resolvable
exc excentric
E extended
f following (eastward
F faint
g gradually
glob. globular
gr group
i irregular
iF irregular figure
inv involved, involving
l little (adv.); long (adj.
L large
m much
m magnitude
M middle, or in the middle
n north
neb nebula
nebs nebulous
neby nebulosity
nf north following
np north preceding
ns north-south
nr near
N nucleus, or to a nucleus
p preceding (westward
pf preceding-following
p pretty (adv., before F. B. L, S
pg pretty gradually
pm pretty much
ps pretty suddenly
plan planetary nebula (same as PN
prob probably
P poor (sparse) in stars
PN planetary nebula
r resolvable (mottled, not resolved)
rr partially resolved, some stars seen
rrr well resolved, clearly consisting of stars
R round
RR exactly round
Ri rich in stars
s suddenly (abruptly
s south
sf south following
sp south preceding
sc scattered
sev several
st stars (pl.
st 9... stars of 9th magnitude and fainter
st 9..13 stars of mag. 9 to 13
stell stellar, pointlike
susp suspected
S small in angular size
S* small (faint) star
trap trapezium
triangle triangle, forms a triangle with
triN trinuclear
v very
vv _very_
var variable
* a single star
*10 a star of 10th magnitude
*7-8 star of mag. 7 or 8
** double star (same as D*
*** triple star
! remarkable
!! very much so
!!! a magnificent or otherwise interesting object
Website Manager: G. Guichard, site 'Amateur Astronomy,' http://stars5.6te.net. Page Editor: G. Guichard. last edited: 3/4/2020. contact us at ggwebsites@outlook.com






















































